- You have no items in your shopping cart
- Continue Shopping
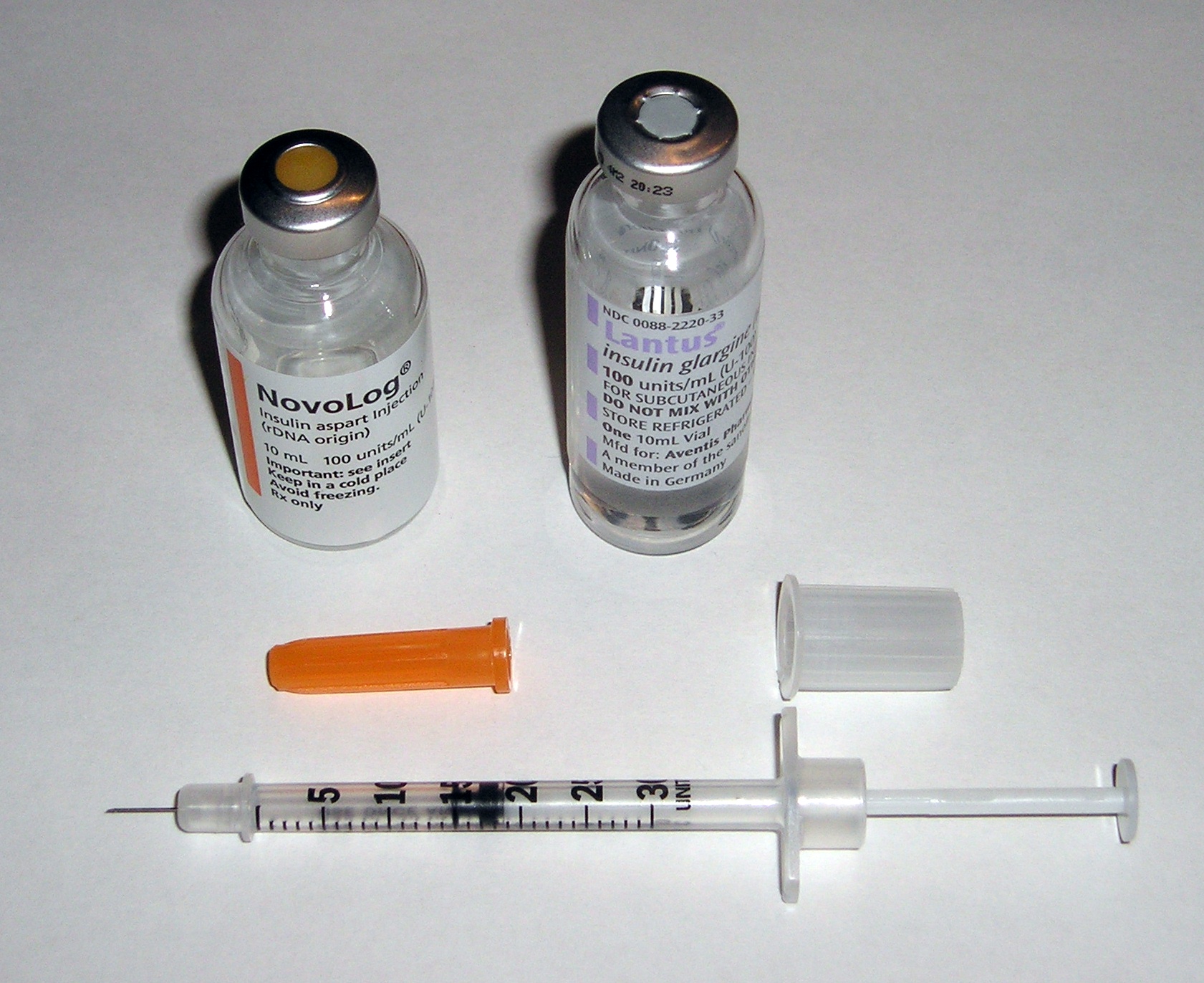
Insulin is a hormone that is naturally produced by the pancreas and is essential for the regulation of carbohydrate, fat, and protein metabolism in the body. It plays a critical role in enabling cells to absorb glucose from the bloodstream, which is then used for energy or stored for future use. Insulin therapy is used to treat diabetes mellitus, a condition characterized by high blood sugar levels due to the body’s inability to produce or effectively use insulin.
Benefits:
- Blood Sugar Control: Insulin helps to lower blood glucose levels by facilitating the entry of glucose into cells, thereby preventing hyperglycemia (high blood sugar).
- Prevention of Diabetes Complications: By maintaining blood sugar within a target range, insulin therapy can help prevent or delay complications associated with diabetes, such as heart disease, kidney damage, nerve damage, and eye problems.
- Improved Energy Levels: Proper insulin action ensures that cells receive the glucose they need for energy, which can improve overall energy levels and reduce fatigue.
- Weight Management: Although insulin is often associated with weight gain, when used appropriately to control blood sugar, it can help in weight management by reducing the amount of sugar in the bloodstream that is stored as fat.
Side Effects:
While insulin is a life-saving treatment for diabetes, it can have side effects, especially if levels are not well-regulated. These may include:
- Hypoglycemia: The most common side effect is low blood sugar (hypoglycemia), which can occur if too much insulin is taken or if a meal is missed. Symptoms can range from mild (shakiness, sweating) to severe (confusion, seizure, loss of consciousness).
- Weight Gain: Insulin can lead to weight gain because it promotes the storage of glucose as fat.
- Allergic Reactions: Some individuals may experience allergic reactions at the site of injection or systemically, which can include redness, swelling, itching, or in rare cases, anaphylaxis.
- Lipodystrophy: Repeated injections in the same area can lead to changes in fat tissue, resulting in lumps or indentations in the skin.
- Insulin Edema: Rarely, insulin therapy can cause fluid retention and swelling, particularly when initiating treatment.
Important Information:
- Insulin therapy should be individualized and closely monitored by a healthcare professional.
- Patients should be educated on how to manage their insulin regimen, including how to adjust doses based on blood sugar levels, diet, and physical activity.
- Regular blood sugar monitoring is essential to ensure that insulin doses are appropriate and to prevent hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia.
- Patients should be aware of the symptoms of hypoglycemia and how to treat it promptly.
- Insulin should be stored properly, as exposure to heat or freezing temperatures can affect its potency.
Disclaimer: This product description is for informational purposes only and does not replace professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always consult your healthcare provider before starting or changing your medication regimen.
You Might Also Like These:
Product Recently View
You have not recently viewed item.











Customer reviews
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.
Write a customer review